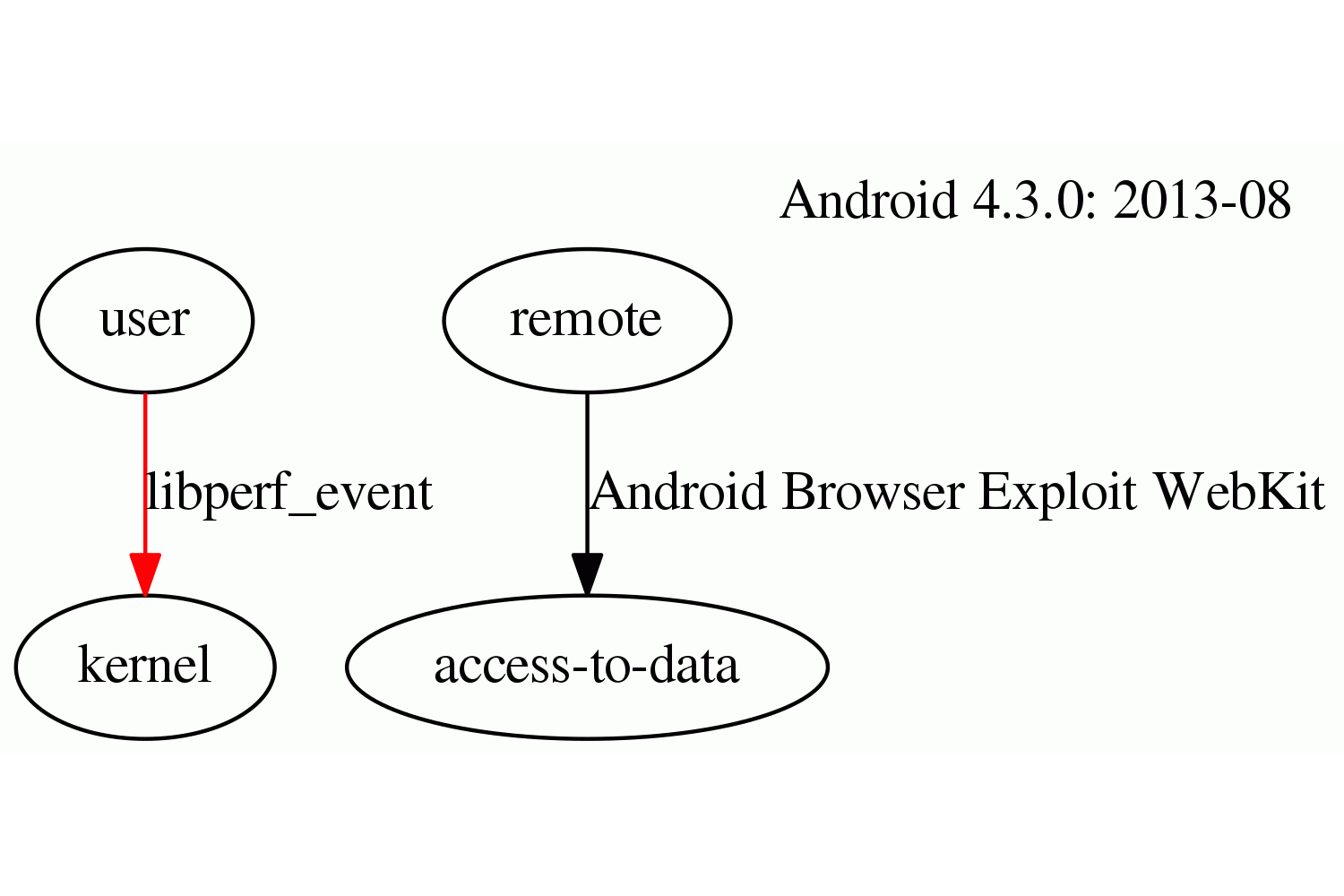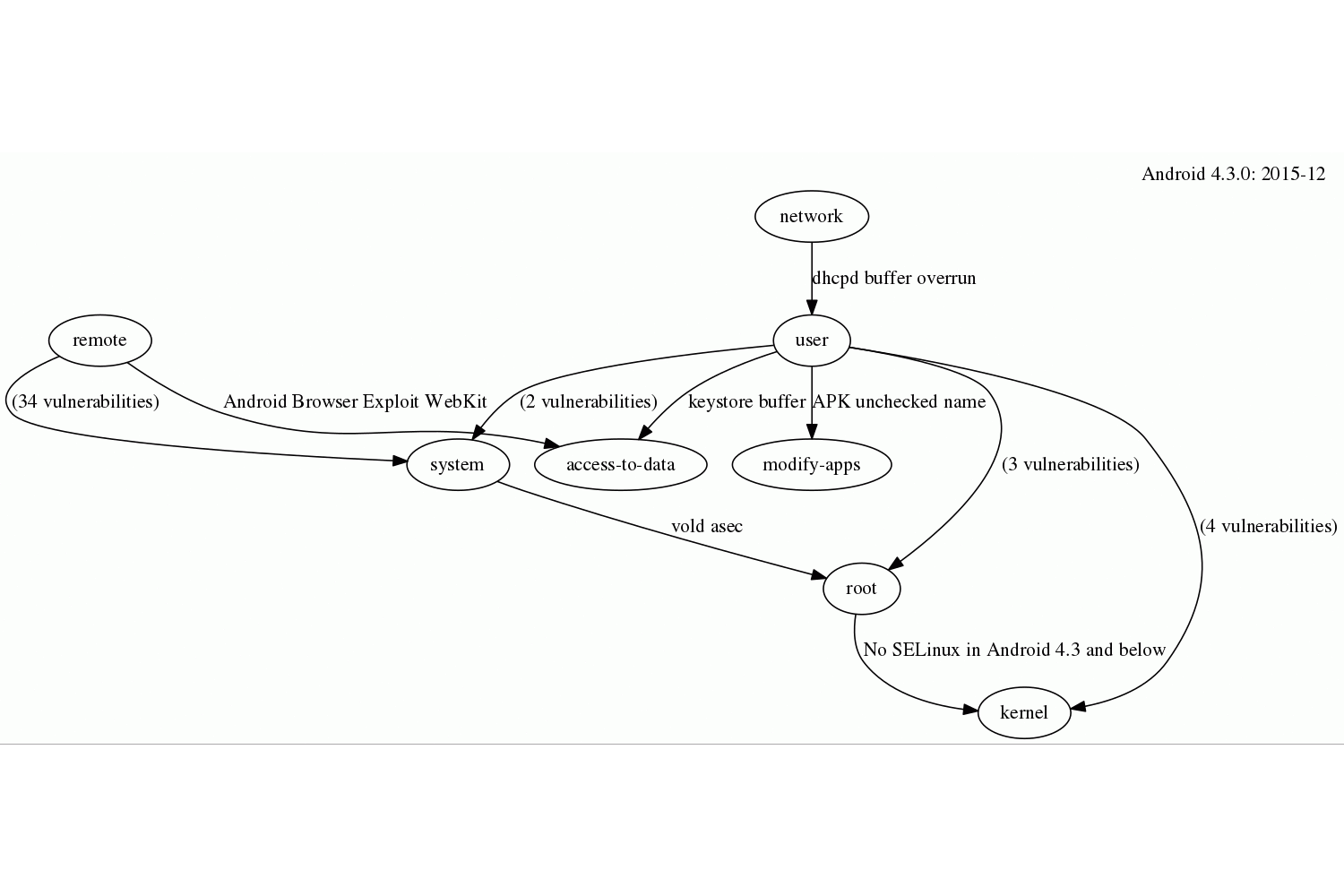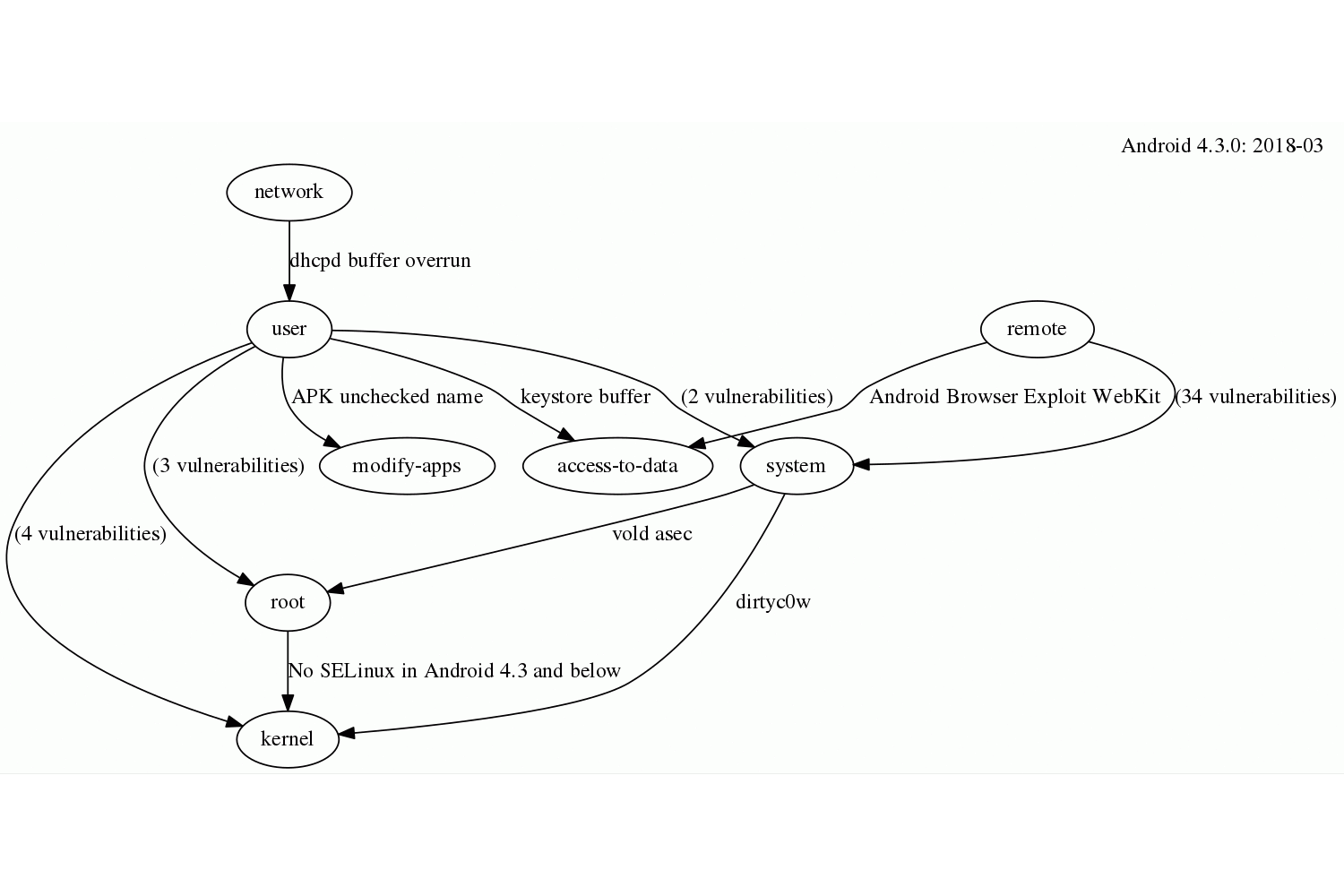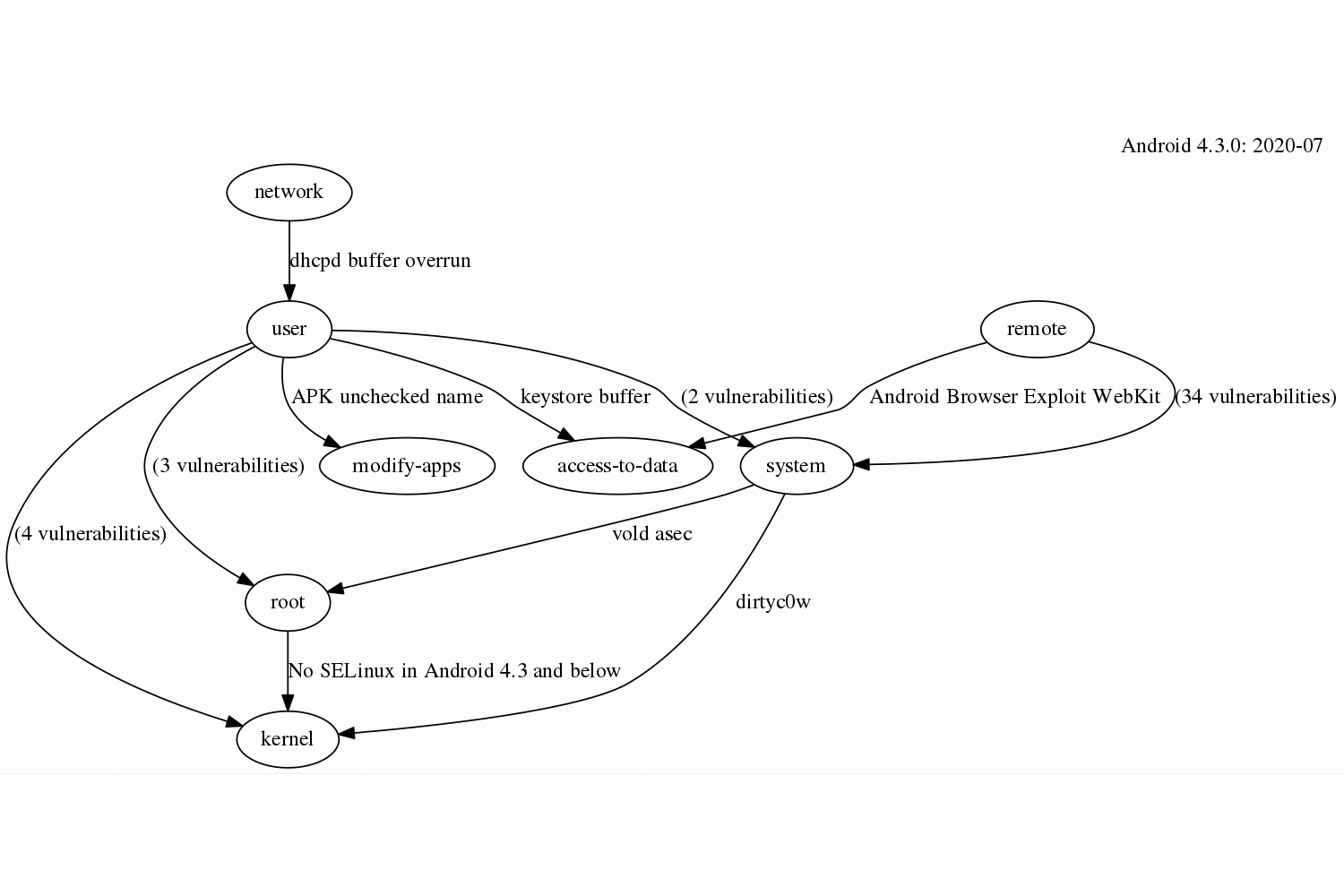
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)
(json)